NLP处理阶段

词法:切分为token
uneasy” can be broken into two sub-word tokens as “un-easy”.
句法:1.检查句子结构有问题与否;2.形成一个能够体现词间句法关系的结果
eg: “The school goes to the boy”
语义:语义是否正确
semantic analyzer would reject a sentence like “Hot ice-cream”
Pragmatic :歧义,中选择一个意思
知识图谱
存储提取的信息的一种方式。存储结构一般包括:a subject, a predicate and an object(主谓宾)

这些技术用于构建知识图谱
sentence segmentation, dependency parsing, parts of speech tagging, and entity recognition.
抽取实体
从句子中抽取主语和宾语,需要特殊处理的是复合名称和修饰词。
抽取关系
从句子中提取“主要的”动词
完成此二者之后便可进行知识图谱的构建,构建时最好将每个关系单独构建一个图谱,这是为了更好可视化。
BERT
适用于少数据集,question answering and sentiment analysis 任务
遮掩形式下的看两边,而Transformer一次可以读取整个token,利用注意力机制学习词间关系。
这里预训练采用的是半监督方式(自监督)eg:完形填空,而微调时采用的是全标注的数据集
输入:一个分类标签[CLS]作为第一输入,随后跟上其他的word序列, 不断向上传,每一层都有注意力,通过前向传播,传给下一个编码器,从最后输出的CLS token.对应的值中可以获得分类信息
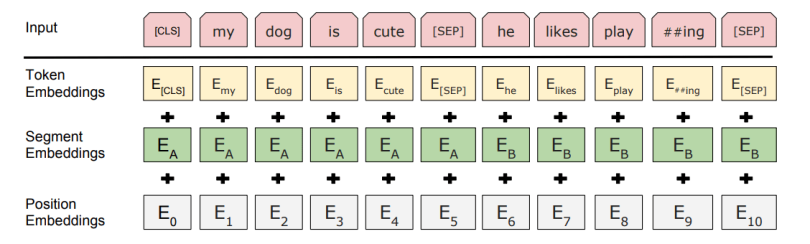
更具体的解释:输入是一下三种Embeddings的累加
the input representation for BERT: The input embeddings are the sum of the token embeddings, the segmentation embeddings and the position embeddings.
- Token embeddings: A token is added to the input word tokens at the beginning of the first sentence and a token is inserted at the end of each sentence.
- Segment embeddings: A marker indicating Sentence A or Sentence B is added to each token. This allows the encoder to distinguish between sentences.
- Positional embeddings: A positional embedding is added to each token to indicate its position in the sentence.
对比:it takes both the previous and next tokens into account at the same time
典型代表:ELMo
工作原理:
训练一个从左到右的正向LSTM:这个LSTM读取句子,对于每个词,它生成一个只包含了左侧上下文信息的表示。
训练一个从右到左的反向LSTM:这个LSTM从句子末尾开始读,对于每个词,它生成一个只包含了右侧上下文信息的表示。
拼接:当需要处理一个词(例如“银行”)时,我们简单地将正向LSTM和反向LSTM在这个词上的输出向量拼接在一起。
非上下文模型,上下文模型(单向,双向)
Context-free models like word2vec generate a single word embedding representation (a vector of numbers) for each word in the vocabulary.
context-based models generate a representation of each word that is based on the other words in the sentence.
“I accessed the bank account,” a unidirectional contextual model would represent “bank” based on “I accessed the” but not “account.” However, BERT represents “bank” using both its previous and next context — “I accessed the … account”
Transformer注意力机制的作用: 理解句中所有词间的关系(by dot),而不是凭借位置关系
For example, given the sentence, “I arrived at the bank after crossing the river”, to determine that the word “bank” refers to the shore of a river and not a financial institution, the Transformer can learn to immediately pay attention to the word “river” and make this decision in just one step.
采用Transformer的解码器,BERT是作为a language representation model,就是将语言转化为计算机能够处理的数值向量
解释15%随机位置(随机发生已经知道了)
To prevent the model from focusing too much on a particular position or tokens that are masked, the researchers randomly masked 15% of the words.
解释15%随机发生
he masked words were not always replaced by the masked tokens [MASK] because the [MASK] token would never appear during fine-tuning.
So, the researchers used the below technique:
- 80% of the time the words were replaced with the masked token [MASK]
- 10% of the time the words were replaced with random words
- 10% of the time the words were left unchanged
BERT实践
处理输入:
1.第一个句子开头加入[CLS],句子间加入[SEP]

2.句子分为token

n. 训练流程